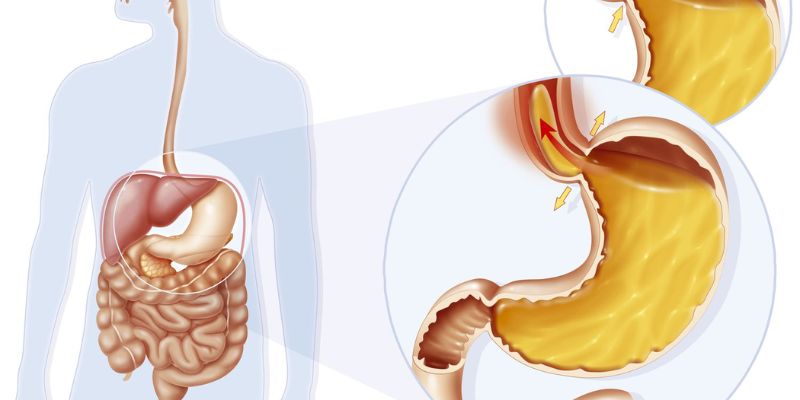
Diaphragm contractions, which divide the chest and stomach, cause hiccups. This abrupt contraction snaps the vocal cords, making the "hic" sound. Your chest, stomach, or neck may contract during a hiccup. These common symptoms frequently go away without treatment. Overeating, drinking, carbonated beverages, and excitement are the reasons why do people get hiccups.
Occasionally, chronic hiccups may indicate a medical issue. Hiccups can cause weight loss and exhaustion if they endure months, affecting everyday life and well-being.
Hiccups are usually harmless and go away independently, but a doctor should check chronic or severe ones to rule out health risks. Understand hiccup causes and strategies to control and reduce this frequent, transient occurrence.
Hiccup Causes and Triggers
Hiccups, involuntary diaphragm spasms, can be caused by several things. Overeating, especially a big dinner, is a typical reason. Hiccups can also result from sudden temperature shifts or excessive temperatures. Extreme emotions like excitement or tension can also cause diaphragm spasms. Carbonated beverages, alcohol, and gum are recognized hiccup and astrid triggers.
Chronic Hiccups and Nerve Irritation
Damage or irritation to the vagus and phrenic nerves, which govern the diaphragm muscle, can cause long-term hiccups. Nerve difficulties might result from hair contact with the eardrum thyroid gland tumors or cysts in the neck. Stomach acid regurgitation into the esophagus, which delivers food from the mouth to the stomach, can also irritate these neurons. Sore throats and laryngitis can cause nerve discomfort and frequent hiccups. Understanding and treating these nerve irritation reasons is essential to ending extended hiccup bouts.
Drug-induced Hiccups
Medication can cause long-term hiccups. Sedatives and anesthetics can interrupt the hiccup reflex. Hiccups have also been linked to steroids like dexamethasone, which reduce inflammation in arthritis, asthma, and renal disease. Other steroids can also cause hiccups.
Alcohol-Related Hiccups
Chronic alcohol usage, a sign of alcohol use disorder, can also prolong hiccups. Alcohol can cause recurrent hiccups by interfering with the central nervous system. It's essential to detect the link between substance use, certain medicines, and prolonged hiccups and get medical help to treat this issue. Understanding why do people get hiccups is essential to solving and ending the problem.
Cardiovascular Factors and Other Influences
Recurrent hiccups can result from uncommon cardiovascular disorders. Hiccups can result from heart attacks and pericarditis. Chronic hiccups can develop from drinking, diabetes, electrolyte imbalances, and renal disease. Steroids, tranquilizers, barbiturates, and anesthesia can produce long-term hiccups.
Hiccup That Lasts Less Than 48 Hours
Hiccups that last less than 48 hours can be caused by several factors, including drinking carbonated drinks or alcohol, overeating, being excited or stressed, sudden temperature changes, and accidentally swallowing air while chewing gum or smoking.
Factors Prolonging Hiccups Over 48 hours
Hiccups lasting more than 48 hours may suggest underlying concerns. Possible causes include nerve injury, inflammation, central nervous system illnesses, metabolic imbalances, and drug addiction. These causes can alter the hiccup and astrid reflex, causing recurrent hiccups that need medical treatment. Understanding the causes and spotting prolonged hiccups is crucial for obtaining medical help and resolving health issues.
When Hiccups Indicate a Problem
Most hiccups are innocuous and resolve on their own. However, recurring hiccups may signal a medical issue. Neurological diseases include stroke, meningitis, tumors, head trauma, and multiple sclerosis, which can induce chronic hiccups. Goiter, laryngitis, stomach reflux, vagus, and phrenic nerve irritation can produce hiccups.
Hiccup Risk Factors
Long-term hiccups are more common in men, suggesting gender is a risk factor. Other than gender, various variables might cause chronic hiccups.
Psychological and Emotional Factors

Hiccups depend on mental and emotional health. High amounts of worry, tension, or excitement can cause long-lasting hiccups. The link between emotions and hiccups shows how interconnected the mind and body are.
Interventions Surgical
Hiccups may occur after abdominal surgery or general anesthesia. After surgery, an anesthetic may affect the physiological functioning of stomach organs, causing chronic hiccups. Understanding these surgery-linked risk factors helps doctors and patients manage and prevent chronic surgical hiccups.
Targeted prevention and medical care must acknowledge these risk variables and their possible impact on long-term problems. Healthcare providers can better understand why do people get hiccups and the illness by addressing these risk factors and devise specific methods to reduce hiccup duration and intensity.
Hiccup Relief Methods
Hiccups might last longer than expected and are usually harmless. Many home treatments can help with chronic hiccups.
Gargle Ice Water
Gargling with cold water for a minute may relieve diaphragm discomfort and stop hiccups. The cool water calms the diaphragm and relieves hiccups.
Suck on a Small Ice Piece
Sucking on some ice might distract you and break the hiccup cycle. Consuming cold might activate throat nerves and muscles, affecting the hiccup response.
Breathing Methods
Breathing slowly into a paper bag might raise your carbon dioxide levels. Increased carbon dioxide may reduce hiccups by relaxing the diaphragm. Holding your breath also produces carbon dioxide and may halt hiccups.
Lifestyle Changes to Reduce Hiccups
If you have frequent hiccups, lifestyle changes may help. Hiccups may be reduced by eating smaller meals and avoiding fizzy drinks and gassy foods. Overeating and hiccups may be avoided with smaller meals.
Seeking Medical Advice

Consult a doctor if hiccups continue or recur. Describe their frequency and length to assist the doctor in assessing your hiccups. Your doctor may recommend relaxation training, hypnotherapy, or acupuncture for chronic hiccups. Explore these possibilities to discover a solution to annoying glitches.
Fetal Hiccups
If you are in a pregnancy baby hiccups in womb, it is natural and not a reason for alarm. The expecting mom is frequently more worried about these cute "hics" than the baby. As your baby's lungs grow in the second trimester, around weeks 23–27, fetal hiccups become more noticeable. Every time your baby hiccups, their whole body reacts, forming a rhythmic pattern that lasts a few minutes before diminishing. A jerking motion or pulsating indicates good growth and development in your baby.
The Truth About Silicone Patches: Can They Really Reduce Wrinkles and Scars Overnight?
Sep 14, 2023
Exploring the Origins of Eczema
Nov 01, 2023

Top 10 Health Benefits of Incorporating Black Beans into Your Diet
Nov 08, 2023

Recognizing Hypothyroidism: Signs and Symptoms
Oct 07, 2023

Effective Shoulder Strengthening Exercises for Robust Musculature
Nov 09, 2023

What is a Posterior Pelvic Tilt
Jul 31, 2023

A Comprehensive Examination of Strategies for Minimizing Visible Leg Veins
Nov 02, 2023

Carbohydrates: Friend or Foe?
Nov 04, 2023